A Comprehensive Overview of the IVF Process
Topic Quick Links

For couples facing infertility, the journey to parenthood can be filled with challenges and uncertainties. In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) has emerged as a groundbreaking solution, offering hope to those struggling to conceive. In this comprehensive guide, we will take you through the IVF process step by step, demystifying the procedure and helping you gain a thorough understanding of what to expect on your path to parenthood.
The IVF process typically begins with an initial consultation with one of our fertility specialists.
During this meeting, you’ll discuss your medical history, previous fertility treatments, and any underlying conditions that might affect the success of IVF. Your doctor will outline the treatment plan, including any required testing, as well as address any questions or concerns. Some required procedures or tests in preparation for IVF may include a high complexity semen analysis or an ovarian reserve assessment.
Getting Started
After the initial consultation, the first step in the IVF process is the ovarian stimulation phase. Your fertility specialist will determine which stimulation protocol is best for you, taking into consideration your age, weight, and ovarian reserve assessment indicators. Your fertility specialist will then monitor your progress through blood tests and ultrasounds to ensure the eggs are maturing as expected. An ovulation trigger will be administered after 10 days of ovarian stimulation when the leading follicles containing eggs reach a diameter of 20mm.
The Egg Retrieval
Once the eggs have reached the optimal size, a minor surgical procedure called egg retrieval is scheduled. This is a minor procedure using transvaginal ultrasound guidance, performed in our in-office operating room suite. This takes about 15 minutes to complete and is done using intravenous sedation administered by our board-certified anesthesiologist.
After the egg retrieval, you will be given medications to suppress your ovary. Expect to begin your menses in 10-14 days. Meanwhile, all of your embryos making it to day 5-7 in the laboratory will be frozen and transferred one at a time starting with your next menstrual cycle.
We do not transfer fresh embryos, so all embryos are frozen at the blastocyst stage. The frozen embryos will be thawed and transferred in the subsequent cycle.
Fertilization
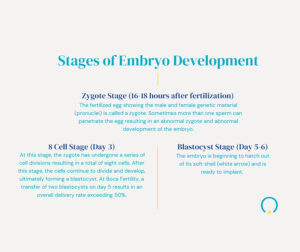
Now that your eggs have been removed from your ovaries, the next step is for the embryologist to prepare your eggs and the male sperm for fertilization. This can be done through traditional insemination or intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI), where a single sperm is injected directly into an egg. After fertilization, the embryos are monitored for development.
The dishes containing the eggs and sperm are placed in embryo incubators. A computer controlled system precisely regulates temperature, oxygen and CO2 levels within the incubators conducive for embryonic growth.
The eggs will be checked 24 hours later to see how many of them were fertilized. You will receive a daily briefing from the IVF nurse coordinator, informing you of the embryos development.
Embryo Culture, Selection and Transfer
The resulting embryos are cultured in a controlled environment for several days, typically five or six. During this time, the embryologist assesses their quality and selects the healthiest embryos for transfer. Any additional embryos may be frozen for future use.
The doctor will discuss with you the number of embryos to be transferred. In general, only one embryo is transferred. The embryo transfer is not painful and takes only a moment to accomplish.
Waiting for Pregnancy
Your pregnancy test will be performed 9 days after the embryo transfer.
If the blood test confirms pregnancy, you’ll continue to work with your fertility specialist to monitor the pregnancy’s progress. If successful, you’ll transition to regular prenatal care with an obstetrician.
Conclusion
The IVF process can be challenging, both emotionally and physically, but it has provided hope and joy to countless families worldwide. Understanding the steps involved can alleviate some of the uncertainty and anxiety that often accompanies infertility. It’s important to remember that IVF outcomes can vary, and multiple cycles may be necessary to achieve success. Schedule an appointment with a qualified fertility specialist at Boca Fertility who can tailor the treatment plan to your specific needs.



